Why is Shunt Resistance dImportant?
Shunt resistance (RshR_{sh}) models leakage current through unintended low-resistance paths across the device (often due to defects, grain boundaries, pinholes in oxides, or poor passivation).
Ideally, RshR_{sh} should be infinite—meaning no leakage.
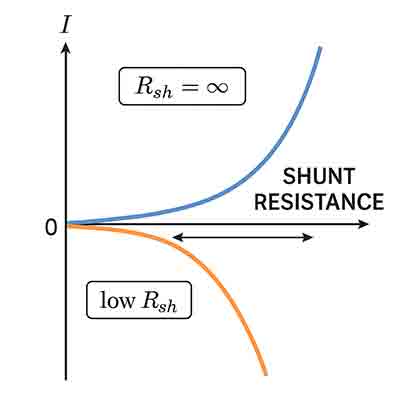
Shunt resistance is an important parameter in semiconductors—especially in diodes, photodetectors, and solar cells—because it represents parasitic leakage pathways that let current "bypass" the intended junction. Here’s why it matters:
Get Your FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
1. In Solar Cells:
- Reduces Power Losses:
- Shunt resistance represents leakage paths that allow current to bypass the p-n junction, causing energy loss.
- A high shunt resistance ensures minimal leakage currents, which is crucial for achieving high efficiency.
- Maintains Voltage Output:
- Low shunt resistance reduces the output voltage of the solar cell, adversely affecting power output.
- Indicator of Quality:
- High shunt resistance is often a sign of good material quality and proper fabrication processes, while low shunt resistance can indicate defects or impurities.
2. In Measurement Systems (e.g., Ammeter with Shunt Resistor):
- Accurate Current Measurement:
- Shunt resistors are used to measure current by creating a proportional voltage drop. Their resistance must be low but precise to minimize errors.
- Prevents Damage:
- By diverting most of the current through the shunt resistor, sensitive measurement components are protected from high currents.
3. In Circuits:
- Controls Leakage Currents:
- In devices like diodes, transistors, or capacitors, unintended shunt resistance paths can allow leakage currents, which degrade performance.
- Improves Reliability:
- Properly designed shunt resistance helps prevent overheating, signal distortion, or energy loss in circuits.
4. In Biosensors, Photodetectors, and CMOS Circuits:
- Enhances Sensitivity and Accuracy:
- High shunt resistance ensures that signal currents are not diverted through unintended paths, preserving signal integrity.
- Minimizes Noise:
- Shunt resistance reduces noise introduced by leakage currents, improving the signal-to-noise ratio.
5. Thermal Considerations:
- High shunt resistance ensures lower parasitic currents, which reduces unwanted heat generation in a system. This is particularly important in applications like power electronics, where heat dissipation can affect longevity and performance.
General Summary:
- High Shunt Resistance:
- Desirable in most applications, especially in energy and precision systems.
- Minimizes unwanted current, improving efficiency and performance.
- Low Shunt Resistance:
- Causes energy loss, lowers efficiency, and may signal material defects or poor design.
Shunt resistance serves as a critical parameter that engineers optimize to balance efficiency, precision, and reliability across various applications.
What is Shunt Resistance?
Shunt resistance refers to a resistive path that diverts or "shunts" current away from a primary path. It is a critical parameter in various electrical and electronic applications, particularly in photovoltaics (solar cells), sensors, and circuit design.
Key Definitions and Applications:
-
In Solar Cells:
- Shunt resistance represents a parallel resistance within the cell. It accounts for leakage currents that bypass the p-n junction.
- High shunt resistance is desirable in solar cells because it minimizes leakage currents, improving the device's efficiency.
- Low shunt resistance leads to power losses as more current is diverted away from the load.
-
In Measurement Systems:
- A shunt resistor is a low-value resistor used to measure current by creating a voltage drop proportional to the current passing through it. This voltage is then measured to calculate the current using Ohm's Law (V=IR).
- Example: In an ammeter, a shunt resistor is used to allow most of the current to bypass the sensitive measurement circuitry.
-
In Circuits:
- Shunt resistance can appear as an unintended effect due to circuit design imperfections or material properties, where leakage currents flow through unintended parallel paths.
Mathematical Description:
For a system with a shunt resistance Rshunt
- The total current through the device (Itotal) is split between the desired path and the shunt path.
The relationship can be expressed as: Itotal=Idesired+Ishunt where Isunt = VRshunt
Importance of Shunt Resistance:
- High R shunt : Reduces unwanted current flow, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Low : Leads to performance degradation and energy loss.
In designing systems like solar cells or precision measurement devices, maintaining an optimal shunt resistance is essential for efficiency and reliability.
n short: Shunt resistance is crucial because it determines how well a semiconductor device suppresses leakage currents. High shunt resistance means better junction integrity, higher efficiency, and more reliable operation.
Would you like me to sketch out a simple I–V curve with high vs. low shunt resistance so you can see the difference visually?
