Semiconductor Manufacturing and Technology
The textbook authored by Michael Quirk and Julian Serda was written to help researchers understand the core technologies behind semiconductor device manufacturing.
We provide high-quality semiconductor wafers to support your research and production needs.
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
From Sand to Silicon - How Semiconductors Are Made
About the Author:
UniversityWafer, Inc. is a leading supplier of Silicon and other semiconductor.
What is a Semiconductor Wafer?
When you look at a circuit board, you'll often see the term "semiconductor." A semiconductor is a material that has an electrical conductivity value between that of a conductor and an insulator. As a result, the resistance value of a device that uses a semiconductor falls as the temperature increases. The opposite is true of metals, which behave in the opposite way. For this reason, it is important to understand the difference between a metal and a substance that behaves as a semiconductor.
A semiconductor is a material that can handle electricity. Its electrons are called carriers and![]() are carried in an electric field. Likewise, holes are the carriers of negative charges. They are used in electronic devices, and they can help with other processes as well. The electrons and holes in a semiconductor contribute to the flow of current. This is why they are called semiconductors. This material also has the ability to control the amount of electricity that it can absorb or emit.
are carried in an electric field. Likewise, holes are the carriers of negative charges. They are used in electronic devices, and they can help with other processes as well. The electrons and holes in a semiconductor contribute to the flow of current. This is why they are called semiconductors. This material also has the ability to control the amount of electricity that it can absorb or emit.
The semiconductor material is a single crystal whose atoms are arranged in a three-dimensional periodic pattern. A pure silicon crystal contains no impurities. Each silicon atom has four outermost orbits, and they share one electron with their neighbors. During the manufacturing process, these electrons are added through a process called doping. Today, the semiconductor industry is estimated to be worth more than $300 billion, and is projected to grow by up to 15% annually.
Semiconductor materials are single crystals in which atoms are arranged in a periodic three-dimensional arrangement. A pure silicon crystal has only traces of impurities. A semiconductor with more holes than electrons is a P-type material. The absence of an electron makes a material a P-type. The simplest of these materials is the diode. A transistor, however, does not have a diode.
The semiconductor industry is a global industry with factories in more than five countries. Each chip is built in a fabrication plant known as a "fab." The process is highly sensitive to temperature variations, static electricity, and tiny particles of dust. A typical semiconductor manufacturing plant costs $10 billion and takes two to five years to complete. A transistor can contain up to ten million transistors. In contrast, a semiconductor chip can have any number of different types of chips.
A semiconductor is a material with different kinds of components. Its properties can be altered by adding different ingredients. A silicon wafer is made of silicon, which is the second most abundant element in the earth's crust. Its shape is shaped like a diamond. A semiconductor is a crystalline material. A thin sheet of silicon has a cubic structure. If the material is a liquid, it is a solid.
Semiconductors are made from silicon. A silicon wafer can have different types of semiconductors on the same wafer. Manufacturers can etch away one layer to reveal the bottom layer. The bottom layer contains the circuitry. The different layers of a semiconductor are called layers. Its shape is like a cake. The layers are used to add different kinds of circuitry. A circuit is created by using this material.
A semiconductor has many components and is very expensive. It has hundreds of billions of transistors. A semiconductor chip can be as large as a Great Pyramid stone. It is used in a lot of everyday products. A silicon chip can hold as many as a trillion transistors. It is the most common type of electronic component. Its name is a type of semiconductor. Its components are called chips.
A semiconductor is a device made from silicon that can be shaped into many shapes. The structure of a semiconductor is made of a ring of electrons. Each electron has a specific number in the ring. An example of a chip is a silicon wafer that is a silicon wafer. It is a material that has a certain structure. It is a material that can be molded into the shape of a diamond.
What are the Steps to Fabricate Semiconductor Wafers?
The book covers the many challenges fabricating microchips on an enormous scale while celebrating the "conceptual simplicity of semiconductor manufacturing."
Think of a tree trunk growing straight up in a tube. A semiconductor starts as a seed that is grown in a cylndical tube called an ingot. Then that ingot is sliced like bread into wafers, also called substrates. These wafes are what is used to create ICs.
Depending on properties added to the ingot during it's grown, the final semiconductor can either conduct electricity or insulate.
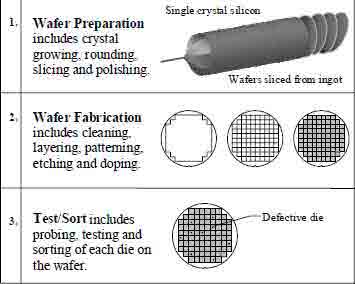
1) Silicon Wafer Preparation
Includes crystal growing, rounding, slicing and polishing.
2) Silicon Wafer Fabrication
Includes cleaning, layering, patterning, etching and doping.
3) Silicon Wafer Testing & Sorting
Includes probing, testing and sorting of each die on the wafer
4) Wafer Assembly and Packaging
A scibe is used to to etch a straight line onto the wafer's![]()
surface before dicing into individual dies. Metal connectioins
are made and the chip is encapsulated.
Electricity is sent through the chip and then it's environmentally tested.
How Did Semiconductor Wafers Come About?
War! The British were boming Germany at night as daylight raids were found to be too dangerous with high loss rates for little to show for it. But bombing at night effectively was problematic as targeting could be off by 5 miles or so. So a new technology was required. The allies were the first to realize the need for a new technology that was first theorized just a decade before.
Luckily for the Allies, the German high command ignored the cries from their scientists and front-line officers regarding the development of the transistor to enhance their radar technology.
Head of the German Luftwaffe Hermal Goering arrogantly proclaimed:
“My pilots,” he bragged, “do not need a cinema on board!”
By the time the Germans discovered what the Allies were working on, it was too late for them.
The war ended and the dawn of the computer age and transister began.
Our future one day may evolve into carbon silicon entities to enhance and extend life. And this is just one of many reason you should know and care about semiconductors.
What is a Semiconductor Chip?
A semiconductor is a material that has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor (such as copper or aluminum) and an insulator (such as rubber or plastic). Semiconductors are used in electronic devices as the basis for transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits.
A chip, on the other hand, is a small piece of semiconductor material (usually silicon) that has been etched or printed with multiple layers of electronic components such as transistors, capacitors, and resistors. The components on a chip are connected by tiny wires or metal traces, which create circuits that can perform specific functions.
In summary, a semiconductor is a type of material with specific electrical properties, while a chip is a specific application of semiconductor technology that contains multiple electronic components and circuits on a single piece of silicon.
What is the difference between a chip and a semiconductor?
A semiconductor is a material that has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor (such as copper or aluminum) and an insulator (such as rubber or plastic). Semiconductors are used in electronic devices as the basis for transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits.
A chip, on the other hand, is a small piece of semiconductor material (usually silicon) that has been etched or printed with multiple layers of electronic components such as transistors, capacitors, and resistors. The components on a chip are connected by tiny wires or metal traces, which create circuits that can perform specific functions.
In summary, a semiconductor is a type of material with specific electrical properties, while a chip is a specific application of semiconductor technology that contains multiple electronic components and circuits on a single piece of silicon.
What is a Semiconductor Company?
A semiconductor company is a business that designs, develops, manufactures, and sells semiconductor components, such as integrated circuits, diodes, transistors, and memory chips. These components are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including smartphones, computers, automobiles, and home appliances.
Semiconductor companies may specialize in particular types of semiconductors, such as memory chips or microprocessors, or they may offer a wide range of semiconductor products. Many semiconductor companies also provide design services and tools for engineers who are designing electronic systems.
Some of the largest semiconductor companies in the world include:
- Intel
- Samsung
- Qualcomm
- Broadcom
- Texas Instruments
- Micron Technology
These companies invest heavily in research and development to create new semiconductor products that are faster, smaller, and more efficient than their predecessors, driving advancements in technology and shaping the future of the electronics industry.
What is a Semiconductor Used For?
A semiconductor company is a business that designs, develops, manufactures, and sells semiconductor components, such as integrated circuits, diodes, transistors, and memory chips. These components are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including smartphones, computers, automobiles, and home appliances.
Semiconductor companies may specialize in particular types of semiconductors, such as memory chips or microprocessors, or they may offer a wide range of semiconductor products. Many semiconductor companies also provide design services and tools for engineers who are designing electronic systems.
Some of the largest semiconductor companies in the world include Intel, Samsung, Qualcomm, Broadcom, Texas Instruments, and Micron Technology. These companies invest heavily in research and development to create new semiconductor products that are faster, smaller, and more efficient than their predecessors, driving advancements in technology and shaping the future of the electronics industry.
Semiconductors are used in a wide range of electronic devices and systems. Here are some common uses of semiconductors:
-
Integrated circuits (ICs): ICs are tiny electronic components that contain many transistors and other circuit elements on a single chip. ICs are used in almost all electronic devices, from smartphones and laptops to cars and medical equipment.
-
Transistors: Transistors are semiconductor devices that can be used as switches or amplifiers. They are a fundamental building block of modern electronics.
-
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): LEDs are semiconductor devices that produce light when a current is passed through them. They are used in a wide range of applications, including lighting, displays, and indicators.
-
Solar cells: Solar cells are made from semiconductor materials that convert sunlight into electricity. They are used in solar panels to generate renewable energy.
-
Memory devices: Memory devices, such as flash memory and DRAM, are made from semiconductor materials and are used to store data in electronic devices.
-
Power electronics: Power electronics devices, such as power transistors and diodes, are used to control and convert electrical power in applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial equipment.
Overall, semiconductors play a critical role in the electronics industry and are used in countless applications that make modern life possible.
