I use used fused silica wafers as substrates for the evaluation of thin films grown on top either by ALD or CVD. What spec do you suggest would work best?
JGS1 Ultraviolet Fused Silica Windows
What JGS1 Fused Silica Spec Works for Thin Film Research?
Fused silica substrates are commonly used in thin film deposition due to their high purity, low thermal expansion, high thermal stability, and excellent optical properties. These properties make them ideal for a range of applications including optics, electronics, and photonics.
We help researchers find the right specs for their projects. Below a Postdoc request a quote on the following:
Postdoc Researcher Question:
The typical material is Fused SIlica JGS1 and the max diameter is max. diameter 200 mm and max. height 100 mm with a nano grade polished finished. Maybe Dia:150mm*6mm will be the best option based on our experience.
Reference #38321 for questions/specs and pricing.
JGS1 is an optical quartz glass made of synthetic stone (SICL-4), a raw material that is melted with a high purity oxygen flame.
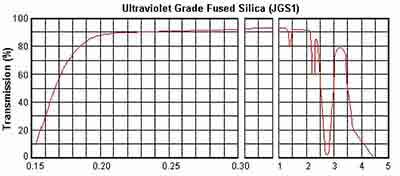
It contains a large amount of hydroxyl (2000 ppm) and has excellent UV transmission. It is an excellent optical material in the range from 185nm to 2500nm. Due to the particle structure, it reaches a strong absorption peak at 2730nm. In the short-wave UV range, its transmission power is better than with other types of glass. At 185 nm, the UV transmission rate can reach 90% or more.
JGS1 Fused Quartz windows are great for the following applications:
- Laser substrate
- Windows
- Lens
- Prism
- Mirror
We have JGS1 Fused Silica Wafers up to 200mm in diameters. Diced pieces are also available and all dimensions can be purchased in small quantities. Buy Online here!
Get Your JGS1 Fused Quartz Windows Quote FAST!
JGS1 Fused Silica Transmission Curve
What Is JGS1 Fused Silica Used For?
JGS1 is a high-quality fused silica crystal, which is perfect for applications that require light transmission at normal temperatures. It is also used in semiconductors and the solar industry, and contains a small number of bubbles. This type of glass is clear and has a low mechanical damping. Its properties make it ideal for a variety of optical applications, including telescopes.
Besides lenses, JGS1 fused silica is a versatile material that is suitable for a variety of high-tech applications. It is highly transparent in both the visible and ultraviolet spectrums and has a low thermal expansion. Because of this, it is also an ideal material for medical devices. Furthermore, this glass is transparent and virtually free of bubbles and inclusions, making it a reliable choice.
JGS1 ultra-violet grade fused silica is a high-purity amorphous silicon dioxide with excellent optical properties. Its excellent transparency in visible and ultraviolet wavelengths makes it an ideal material for lenses. It is highly resistant to temperature change and is the best choice for medical devices. In addition, its optical properties are similar to other forms of amorphous silicon dioxide, making it an excellent choice.
Fused silica is a highly versatile material. It has excellent thermal properties and a high degree of chemical purity. It is a great choice for optics that operate in the visible and deep ultraviolet wavelength ranges. Generally, it is more expensive than its counterparts, but its superior optical qualities make it ideal for a variety of applications. So, if you are interested in using this material in your project, you should consider the advantages it offers.
JGS1 Substrate Specs
| Parameter Value | JGS1 |
| Max Size | <200mm |
| Tramission Range (medium transmission ratio) | 0.17~2.10um (Tavg>90%) |
| OH-Content | 1200 ppm |
| Fluorescence (ex 254nm) | Virtually Free |
| Impurity Content | 5 ppm |
| Birefringent constant | 2-4 nm/cm |
| Melting Method | Synthetic CVD |
Where can you purchase JGS1 Ultraviolet Grade Fused Silica?
JGS1 is more expensive than JGS2 or JGS3. But we have a large selection of JGS1 Fused Quartz Windows in Stock.
What other Fused Silica Windows Grades are Available?
Other fused silica wafer grades and their applications include:
What is JGS1 Fused Silica Wafers?
This high-grade amorphous silicon dioxide is virtually transparent in all spectral regions. It has excellent optical properties, a low thermal expansion coefficient, and is free of inclusions and bubbles. It has excellent transparency in the visible and ultraviolet spectra. There are no absorption bands in the 185-250 nm spectral region. This makes it an excellent material for many applications. Although it is more expensive than other materials, it is a good choice for many applications.
JGS1 Fused Silica is a high-quality amorphous silica that is free of bubbles. This material is transparent in the ultraviolet and visible wavelength ranges. This is a superior option for high-end, critical optics applications. This material is also available in IR and sapphire. It is a very reliable and durable material for medical devices, including endoscopes.
Fused silica is a non-crystalline form of silicon dioxide. It has good thermal characteristics, a low coefficient of thermal expansion, and a very high laser damage threshold. Its optical properties make it a popular material for optical components. There are three types of chinese amorphous silica: JGS1, JGS2 and JGS3. This material is equivalent to Suprasil 1&2 (Heraeus), Spectrosil A and B (Saint-Gobain), and Dynasil 1100 and 4100.
JGS1 Fused Silica is an optical grade amorphous silica, a crystalline form of silicon dioxide. It is very high in purity and has an excellent thermal expansion characteristic. Its high transparency in the ultraviolet and visible wavelength ranges make it an excellent material for optics. It is an exceptional choice for medical devices. The following are the characteristics of JGS1:trecutădized, NQW and X-Ray.
Ultraviolet Grade Fused Silica is a type of amorphous silicon dioxide. This material is highly transparent in ultraviolet and visible wavelengths. It is compatible with most types of glass. It also has high optical performance. It has no bubbles or inclusions. It is ideal for a variety of optical applications. These wafers are compatible with optical grade A, B, and C. They are highly transparent in UV and visible wavelengths.
JGS1 Fused Silica is a transparent crystalline material with high chemical purity. Its low thermal expansion properties make it a perfect material for optical applications. It is also a good choice for optical components. It is suitable for a variety of high-tech applications. This product is available for both domestic and international markets. However, you can find it at your local laboratory. You can also find JGS1 Fused Silica at most major electronics manufacturers.
JGS1 Fused Silica is a non-crystalline material that is available at affordable prices. The price of this type is slightly higher than the cost of JGS2 and JGS3 Fused Silica. The latter is generally more expensive, but it offers more benefits. It is a good choice for optical systems. The crystalline material has good refractors. Further, it is compatible with a wide range of LEDs.
Fused Silica is a versatile material used for high-end optical applications. It is an ideal choice for lenses, prisms, and other applications that require high-quality transmission and sensitivity. In addition to its high-grade characteristics, JGS1 is also suitable for transmitting light and is used for a variety of optical purposes. These include solar cells, photovoltaic panels, and electronic components.
The JGS1 ultra-violet grade fused silica is a high-purity amorphous silicon dioxide. It is transparent in both visible and ultraviolet wavelengths, is free of bubbles, and has a wide temperature range. It is ideal for use in a wide range of optical applications, including transmissive lenses and other materials. The optical properties of JGS1 are similar to those of other amorphous silicon dioxide, and are very stable over a wide range of temperatures.
Fused Silica is a chemical combination of oxygen and silicon. It has the best transmission in the UV spectrum, whereas Quartz is a crystalline silica glass. It is also very stable and has low thermal expansion, allowing it to be used in a variety of applications. It is used in many industries, including optical components. Its light-transmitting capacity, high stability, and low OH content make it ideal for many applications.
JGS1 Fused Silica Research
Silica wafers originally developed to measure the quality of optical coatings. Translucent quartz tubes are often used to coat electrical elements and for a variety of other applications. Also in photovoltaic cells fused UV melt silicones are frequently used, such as those of the JGS1 series. [Sources: 1, 5]
Molten silica forms have excellent thermal and shock resistance and are inert to most elements and compounds, including virtually all acids, except hydrofluoric acid, which is highly reactive even at relatively low concentrations. The most common impurities are hydrogen peroxide and hydrochloric acid (Hydro - H2O), which can influence both the chemical properties of the wafers and their conductivity. Any element that is built into a larger piece will most likely contain bubbles, but applications should not be sensitive to inclusion. [Sources: 0, 4, 5]
Molten quartz is very strong under compression, so the design's compressive strength is well above 1.0, but its tensile strength must be at least as strong as that of a glass wafer, and perhaps even stronger. The tensile performance can be influenced by surface defects, which can greatly reduce the strength of the glass. [Sources: 0]
F Molten quartz can undergo large, rapid temperature changes without cracking, but this is accompanied by a large reduction in density, which leads to cracking and splintering. This limitation can be removed by high cooling with cristobalite, which causes the glass to fall back into a crystalline state under certain conditions. [Sources: 0]
You can send me a drawing or a findal of your product and I will make you an offer and agree with you, or you can send me a description of the material and its properties by e-mail. This material includes materials used in distant ultraviolet and infrared optical fields such as lenses. These lenses are used for UV photography because quartz glass has a much higher resolution than the lenses we produce for high resolution photography in the ultraviolet, infrared and near infrared fields. [Sources: 0, 5]
The birefringence tetragonal crystal structure leads to a difference in the refractive index and the reflection of quartz glass is generally 8. Spectral transmission is much better than with other types of glass and in the infrared range greater than with ordinary glass. In the visible range, the transitions in quartz glasses are also higher, but the ultraviolet range is larger and the infrared range is smaller. A spot that turns white is caused by the refraction of the light of the crystalline material and not by reflection. [Sources: 0, 2]
By adding a small amount of TiO2, the UV light is filtered out at 220 nm, which is called ozone-free quartz glass. Shortwave up to 340 Nm can be filtered out by adding a few micrometers of silicon dioxide (0.1% of the total amount) to quartz glass. [Sources: 2]
A thin article made of quartz glass, which is quenched by immersion in cold water for 1000 dollars to break, is available. Due to the additional risk of thermal fractures, a large number of silicon dioxide - molten quartz - used has been included in the list of the most dangerous materials in the world due to its high temperature, high pressure and high thermal conductivity, as well as the high cost of its use in electronics. [Sources: 0]
F quartz glass has a high thermal conductivity and a wide transparency range, which ranges from near-IR to UV. UV transparency is also used in the semiconductor industry: read-write-read is a kind of memory chip that stores data when the power supply is switched off, but can be deleted after heavy UV exposure. Silicon dioxide, with its wide transparency range, ranges from UV to near IR and has the potential to be used as a cost-effective, powerful and energy-saving storage material. [Sources: 1, 5]
JGS1 can be used in optics that operate in the deep UV and visible wavelength range, as well as in high resolution images. It can also be used in photovoltaics, as the optics work at wavelengths of only 10 micrometers and up to 1,000 nm. [Sources: 3, 4]
In the ultraviolet and visible ranges, JGS1 is transparent and has an absorption band in the wavelength interval of 170 - 250 nm. In the spectral range of 185-250, it has a wavelength range of only 10 micrometers and up to 1,000 nm and is translucent. It combines excellent physical properties with outstanding optical properties, such as high resolution images and low power consumption. J GS1 had or has absorption bands of 170-250 nm at wavelength intervals, but it is opaque and transparent in both the UV and visible ranges. [Sources: 1, 3, 4]
Absorption in the visible band is caused by the presence of transition metal ions and absorption at 2730 nm is an absorption peak of hydroxyl that can be used to calculate hydrate values. In the infrared range, it causes an absorption range of 1,000 - 2,500 nm and has intense OH absorption bands. Compared to JGS1 wafers, the transmission range of the more favorable JGS2 wafer was shifted to longer wavelengths. [Sources: 1, 2]
Sources:
[0]: http://www.optoelect.com/2018/Quartz-Glass_0411/11.html
[3]: https://datasheets.globalspec.com/ps/3050/Dayoptics/97EBC971-CF58-4C00-9FBD-017E286E86E2
[4]: http://www.rising-eo.com/newx1.php?classid=347&infoid=910
[5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fused_quartz