MOSFET Preparation for Researchers
Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) Preparation
The following wafers are a great for MOSFET Preparation and is often used by researchers.
Item #2243 - 50.8mm P/B (100) 0.001-0.005 ohm-cm 280um SSP Prime Grade with 90nm of Thermal Oxide
Please let us know if you can use or if you would like us to quote another spec!
Get Your Quote FAST!
Video Explains How MOSFETs Work!
What this video and learn how MOSFETs work!
What is MOSFET and How it Works?
MOSFETs are semiconductor devices that work by varying the width of a channel. Charge carriers enter the 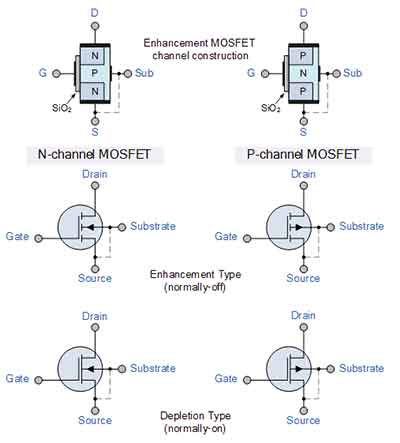 channel from a source and exit it through a drain. The voltage applied to the gate electrode, which is located between the source and drain, controls the width of the channel. The gate electrode is insulated from the channel by a thin layer of metal oxide. There are different types of MOSFETs, which are used for different applications. A positive gate voltage indicates the maximum conductance, while a negative gate voltage decreases it.
channel from a source and exit it through a drain. The voltage applied to the gate electrode, which is located between the source and drain, controls the width of the channel. The gate electrode is insulated from the channel by a thin layer of metal oxide. There are different types of MOSFETs, which are used for different applications. A positive gate voltage indicates the maximum conductance, while a negative gate voltage decreases it.
The gate of a MOSFET is shaped like an "L" shape, with the D leg closer to the S than the G side. The source terminal is connected to the arrowhead on the left-hand side of the symbol. The gate input leg is connected to the D side of the circuit. A "T" shaped gate is also used to indicate the source terminal. The gate of a MOSFET is controlled by the voltage applied to the gate.
An MOSFET is a semiconductor device that functions through a gate voltage. Its channels are made of four different materials: a p-type body (the base of a p-type transistor), an n-type body (the n-type counterpart), and a gate terminal that is connected to the drain. When a negative gate voltage is applied to the gate, holes will be pushed downward through the substrate, and vice versa. Bound negative charges are allied with the acceptor atoms.
The basic operating principle of a MOSFET is to change the state of an electrical circuit by varying the voltage at the gate. The voltage at the gate will change the p-type surface to an n-type surface, where electrons will start to attract larger electric fields. This process is called an inversion, and is one of the most important parameters of a MOSFET. This can be achieved by controlling the Gate-Source voltage and the Gate-Source potential.
The two most common types of MOSFETs are the P-Channel and the N-Channel. The basic structure of a P-Channel MOSFET is a negative-voltage device. The negative voltage on the gate pushes electrons downwards, while the positive charge pushes them upwards. The two modes of a P-Channel MOSSFET are known as enhancement and depletion mode.
The MOSFET device controls the flow of electrons between its source and drain terminals. Its main part is a MOS capacitor. These devices can function as switches, amplification, and switching components. When you are building electronic devices, they can be used in various applications. If you're unfamiliar with the basic functions of a MOSFET, it's time to learn more about this fascinating technology.
During operation, a MOSFET is a semiconductor device that controls current and voltage between its source and drain terminals. Its main component is a MOS capacitor. The MOSFET is a fundamental component of modern electronics. Its applications are many. These electronic components are the main building blocks of the electronic industry. You can create your own designs by combining them with other electrical components and hardware.
The main difference between a MOSFET is the type of dielectric. The former has a metal gate, while the latter is made of polysilicon. A MOSFET has a P-channel, a heavily doped region, and a n-type substrate. A negative gate voltage pushes electrons into the substrate and attracts holes to the p+ region.
A P-Channel MOSFET is made up of negative ions and works with negative voltages. A P-Channel MOSFET's channel conducts when the source and drain are connected to opposite ends. Similarly, a P-Channel MOSFET't conduct when no voltage is applied to the gate. The channel of a MOSFET depends on the MOS capacitor, which is an essential part of the MOSFET.
A MOSFET is a semiconductor device that has three terminals - a source and a drain. Its electrical conductivity is determined by the voltage of the device. A gate voltage is required to turn a P-channel MOSFET on. A gate voltage will turn an n-channel MOSFET off. A negative gate voltage will turn a P-Channel MOSFET on and off.
MOSFET Preparation
This article describes how to prepare an Airsoft Mosfet and how to do it correctly with the help of an expert in the field and a good portion of practice. [Sources: 6]
In this article you will find study notes on Field Effect Transistors, which cover topics such as introduction. Separated Chips 101 have a traditional trench for MOSFETs, which includes several trenches filled with conductive material to form a gate for them. This includes only the trench, which extends in one direction and is revealed in the section on the left side of the page, not on the right. [Sources: 2, 9]
Consequently, there could be an additional epi layer connected to the floating p-column, which in this embodiment comes from the electrode. In addition, the floating layer on the lower layer of the P - body of a MOSFET is connected by a floating P - column. It could be that the transistors are aligned in the p- body and in some embodiments are all rectangular, like the thep columns. [Sources: 5]
Another assembly with a dialectic insulator is the silicon dioxide MOSFET. An alternative material is thermally oxidized silicon, in which the silicon dioxide serves as a gate insulator, but alternative materials can also use other materials such as silicon oxide, silicon carbide or silicon nitride. [Sources: 7, 8]
This device is also called a negative channel MOSFET or NMOS transistor, because the outlet source terminal is doped with donor ions such as phosphorus or arsenic if the substrate consists of the p-type semiconductor material. This device can also be called a positive kanalMOS FET or PMOS transistor, as the substrates are N-types. [Sources: 0]
The conductivity in a MOSFET is generated when the gate source voltage is generated by an electric field. When the source and the PMOS transistor are connected, the output VDS is pulled to the VDD and when logic 1 or 0 is generated, it is pulled to ground. [Sources: 0, 4]
This method involves preparing the MOSFET for switching from wire to blocking mode by applying the first voltage signal, which has a first voltage level, to its shielding and gate electrodes. The second voltages of the signal are placed on the switching door before it is switched from the blocking mode to the line mode. After preparing for the switch from a blocking mode to a line mode, the signals of the second voltage at the gate are returned to the first voltage level. [Sources: 10]
The columns of the first MOSFET chip are arranged in two columns on the second MosFet chip, the columns for the third and fourth columns on each of the two gate electrodes. The column for each column of the two-column M OSFETS chip is located on the second gate electrode. [Sources: 2]
In the case of NMOS transistors, the voltage applied to the gate source terminal is required by the channel that forms the PMOS transistor. In the E-MOSFET, however, a channel connecting the two terminals is physically implanted into the D-OSFETS. [Sources: 0]
Therefore, most of the key indices of power in the E-MOSFET are the same as for NMOS transistors, but with a much lower voltage. This means that no voltage has to be applied to the D - OSFETS in order to be able to switch them on. The E-MOS FET can be used in a wide range of applications as it does not require additional voltage to be switched off. [Sources: 0, 3]
There are two types of E-MOSFET transistors, one with an isolated gate and one without, and there are a number of other types with an isolated gate, such as the D-OSFETS and the NMOS. [Sources: 7]
The first is the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), and the second is the Field Effect Transistor (FET). The Isolated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) has two types of transistors, one with an isolated gate and one without, both with a bipolar gate. [Sources: 8]
The space of a simple MOSFET cell has important parameters for the performance of the Mosfet, including the number of transistors, the voltage and the amount of space available in the cell. The consumption of this type of MosFet is no more than 1,000 watts per square centimetre, but it has an average power of only 1.5 watts and had to have a physically implanted channel for its power supply. [Sources: 2, 9]
To maximize voltage and power drop in the MOSFET and improve the UIS performance of the Trench - Mosfet, the electrical field distribution is altered. In the Miller range (M), the most switching losses occur with a conventional MosFet, which occur when the voltage of the device is relatively high. Vg - SWITCH is controlled and reduced and prepared for the Mosfet-20 to be switched on, while the voltage signal of the VG - SHIELD is reduced to a blocking state. [Sources: 1, 10]
The most commonly used component geometry is a geometry similar to that of a thin film silicon transistor (TFT) that uses thermally grown SiO 2 as gate dielectric. Unlike conventional MOSFET devices, gated MosFet devices have a practically flat Miller region. The body is connected to the source terminal by a series of transistors, each with its own gate, and the body of the device. [Sources: 7, 8, 10]
Sources:
[0]: https://www.intechopen.com/books/complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor/introductory-chapter-complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor-cmos-
[1]: https://patents.justia.com/patent/9704948
[2]: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20180005959A1/en
[3]: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN104658901A/en
[4]: https://blog.oureducation.in/important-questions-on-mosfet/
[5]: http://www.freepatentsonline.com/y2019/0326431.html
[6]: https://smartarmaments.com/blog/complete-airsoft-mosfet-installation-guide
[7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organic_field-effect_transistor
[8]: https://uk.rs-online.com/web/generalDisplay.html?id=ideas-and-advice/mosfet-guide
[9]: https://gradeup.co/field-effect-transistor-study-notes-i-96d9d1d0-79ad-11e7-bf36-f08a68dca14c
[10]: http://www.google.com/patents/US7195979
