What Wafer Do I Need for Nanochip Research?
A graduate student requested help with their research project.
My project pertains to the study of microfluidics and nanofluidics, which has us experimenting with fluid flow through  series of channels (nano and micro in size) on a "chip." We are awaiting the arrival of our precisely-made nano-chip that is being specially made overseas; in the meantime, we would much like to experiment with creating a chip (most likely containing a series of micro-sized channels) in our own laboratory, via FIB (focused ion beam). For our chip, we would like to use silicon as the primary material, and then cover the channels with a glass or polymer.
series of channels (nano and micro in size) on a "chip." We are awaiting the arrival of our precisely-made nano-chip that is being specially made overseas; in the meantime, we would much like to experiment with creating a chip (most likely containing a series of micro-sized channels) in our own laboratory, via FIB (focused ion beam). For our chip, we would like to use silicon as the primary material, and then cover the channels with a glass or polymer.
As you may know more about silicon than we, what silicon would you suggest we use? Each chip would need not be larger than 2" in diameter.
Additionally, we were wondering what the extent of your services are? We saw that you do dicing, polishing, etc.; would you by chance also do bonding?
Reference #323344 for specs and pricing.
We have a large selection of Glass, and gold coated glass slides, as well as other substrates and materials to help you fabricate nanochips.
Get Your Quote FAST! Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
Nanochips Used to Repair Human Organs
Researchers at Ohio State University are developing a nanochip that can change cells inside the body. The technology, known as tissue nanotransfection, can repair tissues and regenerate entire organs. This new technology is completely painless and noninvasive. In the future, nanochips may even be used in surgical procedures, such as heart valve replacement. This is exciting news for those who are in need of an organ transplant, but there are many questions.
Unlike traditional surgery, the process of repairing organs with nanochips involves injecting DNA into the affected organ. The new DNA allows the skin to grow and function properly. Scientists hope to develop this technology and make it practical for clinical settings. After the nanochip technology becomes available, it will be used to treat human patients. It is currently being developed in animal models, and it could be applied to repairing brain damage from stroke and reversing the damage caused by diabetes.
Although this technology is not yet ready for human use, it is already being studied in a lab setting. The IU team has been working on this technology for over five years, and now it's a practical solution for many medical conditions. They hope to obtain US FDA approval next year, which would open the door to human clinical trials. Other potential applications include repairing nerve damage from diabetes and reversing brain injury from stroke.
Video: Repaing Organs with Nanochips
Nanochip Vs Microchip
What is the difference between a microchip and a nanochip? The difference between these two types of computer chips lies in the process of manufacture. A microchip requires a lot of power, while a nanochip is much smaller and requires little power. The two chipsets are similar in size, but their manufacturing process differs. Here are some of the differences between a microchip and a nanoscopic chip.
Microchip is much larger than a nanochip. A nanochip has no external connections. A microchip is a single integrated circuit, while a nanochip is an entire computer chip. The difference between a microchip and a nanochip is the size of the individual components. However, the nanochip is smaller than a microchip, and it is therefore much easier to manufacture. It also requires far less energy and can operate at higher speed.
The first thing to know is that a microchip is a chip that's too large. A nanochip is a tiny integrated circuit that is much smaller. A nanochip is smaller than a microchip. Its size makes it possible for it to function at high speeds. In contrast, a microchip has a much lower power consumption than a nanochip. Hence, a microchip uses much more power.
A microchip is the smallest electronic integrated circuit. It is made of a tiny semiconductor module, about the size of a fingernail. While it can be created in the nanometer scale, the chip itself cannot be. It must be created at an atomic level. This means that the atoms in the material must be manipulated to form the smaller components of the nanochip. The microchip is a minuscule part of a larger electronic chip.
Microchips are much larger than a nanochip, and a nanochip is even smaller. A microchip is a much smaller version of a microchip, and a nanochip is much smaller than a microchip. In the case of a nanochip, the size of the chip itself is only a fraction of the size of a microchip. The real microchip, on the other hand, will be made up of many more layers, and will be measured in millimetres.
In terms of size, the difference between a microchip and a nanochip is only visible when a microchip is measured in nanometers. While the microchip can be created in the nanometer scale, a nanochip is only possible if the chip is created at a microscopic scale. In comparison, a microchip is a passive electronic device with a much larger scale. It is a small device, and it is about the size of a grain of rice.
A microchip is a semiconductor that contains a large number of tiny components. The size of a nanochip is a single atom. In comparison, a microchip is about the same size as a nanochip. As a result, a nanochip is smaller. If it is a small chip, it can be read by a reader that is smaller than a microchip. If a chip is large enough, it would be used in a larger device.
A nanochip is a miniature electronic chip. A microchip is a chip that is one atom wide. A nanochip can be measured as a single unit of the same size as a microchip. As a result, a nanochip is smaller than a microchip, and it is not the same as a microchip. The two types of chips are similar in their use and their functions.
A microchip is a smaller version of a microchip. In fact, it's an evolution of the microchip. A nanochip is more advanced than a microchip, and has a more complex structure. It is a tiny integrated circuit, but it is still a miniaturized computer. It has a smaller surface area, but it has a lot of the same features as a microchip.
A biochip is a series of microarrays placed on a solid substrate. They allow researchers to perform multiple tests at the same time. They work on the principle of hybridization, where nucleic acid molecules attach to a solid surface. The results are then determined. A microchip, on the other hand, is an integrated circuit etched on a silicon chip or a wafer. A microchip uses a single silicon chip as its main component, while a nanochip can be used for a multitude of applications.
The Benefits of the Smallest Microchip Available
 The smallest microchip is about nine nanometers in size, and it is designed to be injected into a human body using a hypodermic needle. While it is still too small for human use, it does have significant advantages over its larger counterpart. It can measure vital signs and monitor body temperature. Hopefully, this development will lead to the development of smaller microchips for future use. But until then, let's explore some other ways the smallest microchip can be beneficial.
The smallest microchip is about nine nanometers in size, and it is designed to be injected into a human body using a hypodermic needle. While it is still too small for human use, it does have significant advantages over its larger counterpart. It can measure vital signs and monitor body temperature. Hopefully, this development will lead to the development of smaller microchips for future use. But until then, let's explore some other ways the smallest microchip can be beneficial.
IBM recently introduced a chip with 50 billion transistors, which is approximately the size of two strands of DNA. This chip represents an important step in chip technology, as it has 45% more performance while using 75% less energy. While it will have a profound effect on future computing, it won't make a dent in the worldwide chip shortage. But the industry will not rest until it has the smallest microchip available.
In addition to its potential in medical applications, the smallest microchip available will improve the safety of life-saving medical equipment. Currently, implantable microchips can be quite dangerous. That's why it's important to find out more information about the risks and benefits before undergoing surgery. For now, this new technology is only in the laboratory and should only be used for testing purposes. If successful, it will provide a significant benefit for patients.
What is a Nanochip?
A nanochip is a type of microchip that is built using nanotechnology, which involves the manipulation of materials at the atomic and molecular level. A nanochip is typically much smaller than a traditional microchip, with dimensions measured in nanometers (billionths of a meter).
Like traditional microchips, nanochips are made of semiconductor materials and contain a network of transistors and other electronic components. However, due to their small size, nanochips are able to offer higher levels of performance and functionality than traditional microchips.
Nanochips have the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries, including electronics, healthcare, and energy. They may be used in the development of new types of sensors, medical devices, and other technologies that require high levels of precision and performance.
However, the development of nanochips is still in the early stages, and many challenges must be overcome before they can be widely adopted. These challenges include issues related to manufacturing and cost, as well as the need to develop new technologies and techniques for designing and testing nanochips.
What Do Nanochips Look Like?
Nanochips are tiny, computer-like chips, and they are becoming a popular way to create storage devices for mobile devices.
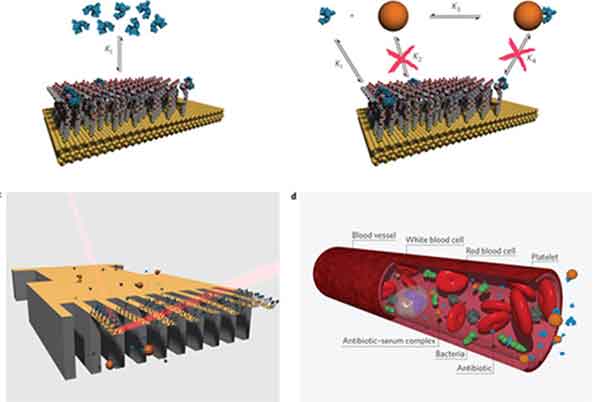
A nanochip is an electronic integrated circuit made of tiny components, which are measured on the nanometer scale. Current technology can create the components of a chip at a Nanometer scale, but it can't make the whole thing. In order to create a complete chip, each component must be made on an atomic level. That means that each atom of material must be altered in order to create tiny components. This process can take several years, and is very expensive.
Nanochip Size
A nanochip is a very small electronic integrated circuit. Because of its size, a nanochip requires a very high level of precision to operate properly. This technology is similar to IBM's Millipede, which was abandoned in 2006, and is backed by various VC firms. It has been working on the array probe technology since 1996, but the company's name is more interesting and gets more media coverage than IBM's.
Using these microchips, the company whose name is Nanochip, is working on a new technology called carbon nanowires. These devices are highly conductive and can't be manufactured using traditional photolithography. As a result, these chips must undergo two steps to be made. However, they can be made to be the size of a micro SD card. Eventually, the entire computer system will be made with nanochips.
A nanochip is an electronic component that is very small compared to a microchip. A nanochip is a small integrated circuit, but it's big in terms of physical dimensions. The entire package of a nanochip is only a few nanometers across - just a few millimeters long. The entire structure of a nanochip is only a couple of hundred micrometers across, but a single component can be hundreds of times smaller than a typical PC.
Despite being small in size, nanochips are still a crucial technology in electronics. They are the tiny digital devices that can perform complex tasks. They are also smaller than a human hair, which makes them the most powerful electronic devices ever. They are not the only type of chips, but they are the most compact. This means that they can be easily stored in smartphones and other mobile phones. They also have much better energy efficiency.
Although it may seem like science fiction, nanochips are tiny in terms of size. They can't be seen in your hand, but they're tiny enough to be detected. The smallest chip in your pocket or purse is only a few hundred meters tall, but you can easily see traces of it on your skin. This tiny tool can be a vital part of your body. You can also use it to repair damaged tissues.
In addition to computers, nanochips can make human life more realistic. In the future, people will be able to use a chip the size of a microSD card. The company behind these chips, whose product is called Nanochip, plans to make this technology a reality. When it's finished, it will be made up of a tiny package, which is just a tiny component of a larger chip.
A nanochip is a tiny integrated circuit, which is very small in physical terms. Engineers have always sought to miniaturize electronic components. A small chip can be more effective and efficient, and use less energy. It can also make it easier to produce smaller versions of electronic devices. Its small size allows it to fit more information in a tiny space. A nanochip can be a very useful technology in the future.
Nanochips are a valuable tool for gene therapy. It's possible to use them in a variety of applications. Among these are medical diagnostics and surgical procedures. The technology is becoming more sophisticated, and scientists are learning about the many applications for this technology. Aside from using these chips, nanochips can also be used for DNA research. Moreover, it's an essential part of everyday life, from helping people to managing cancer.
Innovative Materials Need to Fabricate Nanochips
New York University researchers have reported an innovative technique for fabricating atom-thin computer processors. This discovery may have far-reaching consequences for nanoscale chip production. In addition to improving on traditional semiconductor fabrication methods, scientists are also exploring the use of 2D materials to create ever-smaller and faster chips. The study's findings were published in Nature Electronics. Read the full article to learn more about the new method.
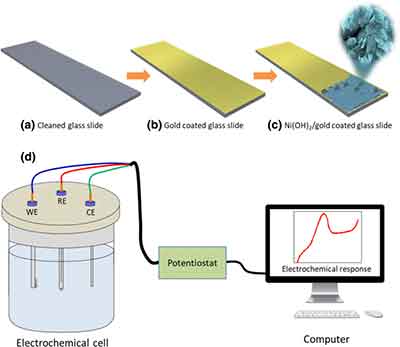 The t-SPL is a breakthrough in fabrication, potentially taking most fabrication outside the clean room. The new method runs on standard 120-volt power, and could revolutionize chip design and materials science. The t-SPL could eventually replace the need for expensive lab facilities and become ubiquitous in research laboratories. The potential is huge, and its application is incredibly exciting. For now, it remains a pipe dream, but once the technology is commercialized, it could be a game changer.
The t-SPL is a breakthrough in fabrication, potentially taking most fabrication outside the clean room. The new method runs on standard 120-volt power, and could revolutionize chip design and materials science. The t-SPL could eventually replace the need for expensive lab facilities and become ubiquitous in research laboratories. The potential is huge, and its application is incredibly exciting. For now, it remains a pipe dream, but once the technology is commercialized, it could be a game changer.
The goal of today's technology is to make nanochips so small that they fit onto a micro SD card. The result could be computers with thousands of times the power of today's computers. The materials used in manufacturing would be relatively cheap and the energy needed to power them would be negligible. One of the first advances in chip design is the reduction in size. The ability to build such chips is crucial for the future of the electronics industry.
A recent study has revealed a new kind of transistor that could revolutionize the electronics industry. Instead of relying on conventional semiconductors, the new type of transistor would send electrons through gaps in the air, which is far faster and less susceptible to heating. It could also revolutionize the way we use electronics. These new devices would be made from various types of materials and could be found in many consumer products. This breakthrough has the potential to transform the way we live.
The nanochip is a tiny integrated circuit. It is extremely small in both physical and atomic scales. Engineers have always sought to achieve the ultimate miniaturization of electronic components. The smaller the components are, the greater the amount of processing power they can accommodate. The smaller the components are, the faster the electronics will be. Similarly, the smaller the size of the components will make the entire package of the nanochips cheaper to manufacture.
The nanochip is an integrated circuit that is incredibly small in both dimensions and weight. As a result, it is extremely small in size. Its design is highly optimized and efficient. Its tiny size will help scientists develop new devices that can be used in everyday life. Ultimately, this new technology will revolutionize the field of electronics. The future of the semiconductors is very bright. And, the t-SPL will allow researchers to fabricate nanochips without the expensive clean rooms and equipment required to manufacture them.
Nanochips can be fabricated by a number of techniques. The process of fabrication is usually done by using a 3D printer or a specialized machine. The process requires very little energy and a lot of materials. In addition to the t-SPL technology, the t-SPL has other advantages that can further enhance the development of the industry. These machines will run on a standard 120-volt power source, which means they are suitable for almost any research lab.
The t-SPL fabrication system can reduce power consumption and require no high-energy electrons or ultra-high vacuum. This new technology could be widely used in industries and could eliminate most of the fabrication processes in clean rooms. It could become a common fixture in research labs. Its versatility and ease of use make it ideal for small scale manufacturing. In addition to its advantages, t-SPL is a useful tool for developing nanochips.
A t-SPL system can eliminate the need for high-energy electrons and ultra-high vacuum. The t-SPL system could be easily scaled up for industrial production and could revolutionize nanochip manufacturing. Its versatility makes it a good choice for research labs, and researchers will be able to use it anywhere. It is not as expensive as the traditional clean room, and it is ideal for manufacturing in clean rooms.
What Are Nanochip Applications in the Human Body?
If you're interested in finding out more about the applications of a nano chip in the human body, this article will give you the lowdown. Read on to learn more about the size, weight, and functions of a nano chip. It's a wonder that nanotech isn't already available for humans, but that's soon to change. Here are some reasons why:

Researchers from the Ohio State University have successfully converted skin cells into nerve cells and muscle cells using nanochip technology. They believe that this technology could be applied to other types of tissue, such as muscles, as well as the treatment of chronic diseases. The researchers also hope to gain FDA approval within the next year, which will enable them to test their new device on humans. Once approved, the nanochips could help treat chronic and acute tissue damage.
Although nanochips are tiny enough to fit in the palm of a hand, it is difficult to visualize them. They can only be detected by a special sensor, but they can be traced on the human body. They could also play an important role in the body when used to repair damaged tissue. As they can be seen on the skin, nanochips could be a life-saving option for many people.
Another useful application of nanochips in the human body is gene therapy. Nanochips are miniature arrays of nucleic acids that allow researchers to perform a number of tests at once. These arrays work on the principle of hybridization, where the nucleic acid molecules attach to a solid surface. The results of the tests are then determined by hybridization. Nanochip technology is becoming increasingly advanced as scientists discover the numerous applications of nanochips.
Despite the numerous applications of nanochips in the human body, it is important to note that these devices will not be available for sale immediately. The technology is not yet mature enough for implanted implants. However, researchers continue to work on this field and are confident in their abilities. However, these technologies are not without risk. There are numerous safety issues to be overcome before these implants are put into use. MRI problems, infection risks, and corrosion are just some of the issues that need to be overcome before these implantable devices can be adopted by the public.
What is the Size of a Nanochip?
There are many pros and cons of using an artificial intelligence chip in human bodies. While it is possible to make these devices more efficient and practical, many experts believe that their size makes them unsuitable for human use. The size of a human cell is about 10 square micrometers, and it is estimated that hundreds of today's smallest transistors could fit within it. By 2020, this number could reach 2.500 transistors.
While most of us are too frightened to think about implanting a tiny chip in our bodies, researchers at Columbia University have created the smallest chip ever made. The motes, which are less than a cubic millimeter, operate as a single chip system. They are implantable via a hypodermic needle and can monitor glucose levels and oxygen saturation in the body. Currently, these chips are only tested in lab rats, but they could one day be implanted into humans.
Researchers have developed silicon chips that are smaller than cells. The team used a variety of methods to collect these tiny chips and internalize them. This new technology could eventually be used to detect diseases and develop new cellular repair mechanisms. A significant advantage of intracellular silicon-based chips is the unending possibilities for design. This new technology will allow for accurate characterization at the single cell level and real-time monitoring of cellular events. It will also allow for precise drug delivery within a target cell.
As a microchip, a nanochip is a passive electronic device that is a fraction of the size of a human hair. Its components are hundreds of times smaller than the average computer's CPU. In a human body, a nanochip may be about the size of a grain of rice. This is a huge benefit for human health. The human body is a vastly complex organism, and nanochips are likely to improve the performance of its components.
What is the Weight of a Nanochip?
Researchers have been testing the effect of a nano chip implanted in the human body on weight and body temperature, and now they are working to make this technology work in human patients as well. Researchers have found that the tiny chip can change the activity of the brain's pleasure center to reduce obesity and promote health. The system has been tested on mice, but is now moving into human trials for morbid obesity. In the current study, Columbia researchers recorded electrical activity in the nucleus accumbens of a human with uncontrollable OCD and found that the implantable chip could change the electrical activity.
Scientists at Columbia University have created the world's smallest microchips, known as motes. These microscopic chips are about the size of a dust mite and measure just 0.1 cubic millimeter. They are implantable into the body via a hypodermic needle, and work as single-chip systems. Scientists have so far tested them on lab rats, but hope to use them in humans one day. These chips could monitor glucose levels and oxygen saturation in human body tissues, enabling remote monitoring of biomolecular processes and weight loss.
What are Nanochip Functions?
Researchers at Indiana University School of Medicine have discovered that nanochips can change the function of tissue inside the body using the process of "nanotransfection," which involves the delivery of specific genes through a harmless electric spark. In laboratory tests, these nanochips were able to transform skin tissue into blood vessels, helping to repair a badly injured leg. The researchers hope to develop the technology for use in various therapeutic treatments and to restore human organs.
A nanochip is a passive electronic device made up of thousands of microchips. These microchips are hundreds of times smaller than a grain of rice. The size and structure of nanochips makes them ideal for use in many applications. The size of a nanochip makes them ideal for implanting into the human body. These microchips can be implanted into various parts of the body. These chips are even used to monitor body functions, such as heart disease and diabetes.
The human liver contains capillaries called sinusoids, which play a major role in liver function and disease. Du et al. replicated key structures of the liver tissue on a microfluidic chip by co-cultivating four major cell types in the chip. They also observed enhancement in liver-specific functions, which they attributed to signaling between the four cell types. These researchers also hope to develop these nanochips for use in medical research.
These chips could be used to test the safety of pharmaceutical drugs. Researchers hope to use organ-on-chip systems in clinical trials in the near future. Such chips are designed to emulate the physiological response of human cells to drugs. The data collected from these chips could help them determine whether certain drugs are safe for humans to use or not. In addition, they can help assess the safety and efficacy of food ingredients. And they can help determine whether certain cosmetic products are safe for the human body.
What Are Nanochip Health Risks?
The insertion of nanochips in the body has raised questions about their safety. Nanoparticles are an increasing concern because of their potential health risks. Researchers have identified a mechanism through which nanoparticles can damage the lungs, and demonstrated a method for blocking this. However, there are some potential issues that need to be considered before making this determination. Here are a few potential health risks. Nanoparticles can trigger inflammation and change the makeup of tissues. They can also influence genes inside cells.
One of the main concerns about injecting such devices into the body is the possibility of infections and damaging MRI equipment. The FDA has warned against implantation of such devices in the body because of electrocution hazards. Also, using this device can lead to complications to the persons health, including corrosive damage to the chip portion. Despite that, the benefits of the microchip are too much to be ignored.
The risks from nanoparticles are pervasive, affecting whole organs. There are cases of nanoparticles causing damage to tissues, which is attributed to cell or molecular defects. In addition, the organs affected were more frequently higher-level organs. In one study, researchers placed carbon nanotubes into lungs, which led to lung inflammation. There are several other possible health effects that nanoparticles may have on humans.
Another kind of nanotechnology is tissue nanotransfection. This is another type of nanochip, which has the capability of reprogramming tissues using an innocuous electrical spark. This device allows doctors to transfer a particular gene to the patient without requiring an invasive procedure or a hospital visit. In this scenario, a chip can be placed in the patients body at the point of care.
Researchers are hoping to start clinical trials next year.
What is the future of nanotechnology and nano-machines?
Nanotechnology is a fast-growing field involving the study and application of very small structures and devices, on the nanoscale (which is approximately 1-100 nanometers). Nanomachines are devices that work on a nanoscale, with potential applications across a range of fields, including medicine, energy production, and materials science. The future of nanotechnology and nanomachines is likely to be shaped by many factors, including advances in technology, changes in social needs and values, and availability of funds and resources. Medicine: Nanomachines may be used to deliver drugs directly to particular cells or tissues within the body, or perform cellular-level surgery.
Energy Production: Nano-machines could be used to improve energy production efficiency, such as more effectively capturing and storing energy, or converting energy from one form to another. Materials science: Nano-machines could be used to make new materials that have enhanced properties, for example, increased strength, durability, or conductivity. Environmental remediation: Nano-machines could potentially be used to clean hazardous materials or contaminants from the environment. Overall, the future of nanotechnology and nanomachines is likely to include a broad array of exciting and potentially transformational applications, and will be dependent upon continued R&D efforts.
- Medicine: Nano-machines could potentially be used to deliver drugs directly to specific cells or tissues in the body, or to perform surgery at the cellular level.
- Energy production: Nano-machines could be used to increase the efficiency of energy production, for example by capturing and storing energy more efficiently or by converting energy from one form to another.
- Materials science: Nano-machines could be used to create new materials with improved properties, such as increased strength, durability, or conductivity.
- Environmental remediation: Nano-machines could potentially be used to clean up hazardous materials or contaminants in the environment.
Overall, the future of nanotechnology and nanomachines is likely to include a broad array of exciting and potentially transformational applications, and it will be dependent upon continued R&D efforts.
How do you combine, connect, compress, merge metal atoms and electricity electric current electrons to make a small little ultra-nanotransistor for nanochips, nanomicrochips, and nanom microcircuits?
This is a fantastic and ambitious question—it hits at the heart of modern nanotechnology and semiconductor device physics! Let’s break down the fundamental concepts, what’s physically possible, and how scientists actually combine metals, electric currents, and electrons at the atomic/nanoscale to create ultra-small nanotransistors for nanochips and nanomicrocircuits.
1. What is a Nanotransistor?
A nanotransistor is a transistor (a basic switch for electricity) that is built on the nanometer scale (1 nanometer = 1 billionth of a meter). These are the building blocks of nanochips (integrated circuits at nanoscale) and are found in today’s advanced computer processors and memory chips.
2. Key Ingredients:
To build a nanotransistor, you generally need:
-
Semiconductor material (commonly silicon, but can be other materials like germanium, gallium arsenide, or even 2D materials like graphene/MoS₂)
-
Metal contacts (for the source and drain)
-
Gate electrode (controls the flow of electrons)
-
Dielectric (insulator between the gate and semiconductor)
-
Electric current (movement of electrons or holes)
3. How Are They Made?
Let’s walk through the process in steps:
A. Combining Metal Atoms & Semiconductors (Fabrication)
-
Start with a substrate (e.g., a silicon wafer).
-
Define nanoscale features using lithography (e.g., electron beam lithography for sub-10 nm features).
-
Deposit metal atoms using physical vapor deposition (PVD), atomic layer deposition (ALD), or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to form source and drain contacts.
-
Pattern the gate electrode using similar techniques, often with metals like tungsten or titanium nitride.
B. Creating the Transistor Channel
-
The channel is the region between the source and drain where electrons flow.
-
In advanced nanotransistors, this channel can be just a few nanometers wide, sometimes even a single layer of atoms (as in carbon nanotube or graphene transistors).
C. Insulation and Gate Control
-
Gate dielectric (ultra-thin layer, often high-k materials like hafnium oxide) is deposited to insulate the gate from the channel.
-
The gate is layered on top—when voltage is applied, it controls the movement of electrons in the channel.
4. Connecting and Merging: Bringing in Electricity
-
Once the device is fabricated, metal contacts allow you to connect an external circuit and apply voltages/currents.
-
Electrons are supplied by applying a voltage across the source and drain.
-
The gate voltage modulates the channel—turning the current ON or OFF.
5. Compression and Miniaturization
-
“Compression” here refers to pushing the device features down to the nanoscale—done through:
6. How the Pieces Work Together:
-
Metals: Provide electrical contact—inject and collect electrons.
-
Semiconductor channel: The path for electrons, controlled by the gate.
-
Electricity/Electric current: Flows through the device when the gate allows.
-
Gate electrode: Controls the flow using a voltage, acting like a nanoscale switch.
7. Ultra-Nano Examples
-
FinFETs: 3D transistors where the channel is a thin “fin” of silicon.
-
Nanowire transistors: Channel is a single nanowire, surrounded by gate.
-
2D FETs: Channel is a single layer of atoms (e.g., MoS₂, graphene).
-
Single-atom transistors: Extreme research, using a single atom as the channel!
8. Can I Build One at Home?
Realistically, building nanotransistors requires billion-dollar cleanrooms and sophisticated equipment. But the principles above are the same, whether you’re at Intel, IBM, or in a university lab.
9. In Summary—Recipe for a Nanotransistor:
-
Choose your substrate (e.g., silicon or 2D material)
-
Pattern nanoscale features (e.g., lithography)
-
Deposit metal atoms for source, drain, and gate contacts
-
Form an ultra-thin channel for electrons
-
Insulate the gate with a dielectric
-
Connect to external circuit for current flow
-
Apply voltages to control the electrons—that’s your nano-switch!
10. Want to See Diagrams?
If you’d like, I can generate or show you illustrations of a typical nanotransistor structure—just ask!
TL;DR:
You combine metal atoms (for electrical contacts) and semiconductor channels at the nanoscale, use sophisticated deposition and lithography, then connect them so electric current (electrons) can be switched on/off by a gate voltage—making a tiny, fast, efficient nano-transistor for future chips and circuits.

