For our customers the orientation of both the <100> and <110> crystal axes are of great importance. The specs for 100mm wafer are summarised below: Prime quality Si <100> substrate Type= SSP Quantity= 10 wafers for initial trail Diameter= 100mm Thickness= 525um (+/-25um) Doping= P/Boron (or whatever you recommend is best for Si V-Grooves?) Resistivity=15-25 Ohm (or whatever you recommend is best for Si V-Grooves?) TTV= 3um Max Bow=15um Max warp=15um Alignment of wafer flat relative to <110> crystal plane, 1𝛔= 0.1° Orientation of wafer surface relative to <100> crystal plane, 1�= 0.1° 1𝛔= standard deviation within wafer Any advice you can provide on the best wafers to use for fabricating Silicon V-Grooves using KOH/TMAH wet etching would be greatly appreciated.
Silicon Subtrates Used For Wet Etching
What Silicon Wafer Spec Use For Fabricating Silicon V-Grooves Using KOH/TMAH Wet Etching
A R&D project manager for a large firm requested help for the following quote:
We are interested in purchasing some bare Si wafers for fabricating Si V-Grooves.
Reference #279305 for specs and pricing.
Silicon Wafers for KOH Wet-Etching
A materials researcher requested a quote for the following:
Can you please send me the quote of 5 3" <100> silicon wafers with 500 nm thick SiO2? The wafers will be used for KOH wet-etching process, so the resistivity is probably not my main concern at this moment. Thank you very much.
Reference #92076 for specs and pricing.
Get Your Silicon Wafer Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
Chemical Wet Etching On Glass To Create Channels
The head of a research lab requested a quote for the following borofloat 33 wafers.
We are interested in a quotation for
- circular borofloat 33 glass wafers, 3 inch diameter, aprox. 350 - 400 microns thickness.
We want to do wafer - bonding (anodic bonding) on (3 inch) Silicon wafer with (3 inch) Glass wafers. We want similarity between silicon wafers and glass wafers regarding diameter and thickness. We will perform chemical wet etching on the glass (for channels) and also metallic electrodes patterning.
Please specify the characteristics of the type of circular borofloat 33 glass wafers that you can provide, along with the quotation.
Reference #194983 for specs and pricing.
Silicon Wafer Wet-Etched To Ring Size
A PhD candidate requested a quot for the following:
I am interested in silicon wafers, wet-etched to ring size of 6/6.8mm (inner/ outer diameter). Do you offer such services? Thank you in advance for your time.
Please quote supplying the wafers and wet etching them into rings. The most important specs are the flatness, roundness, and concentricity of the rings.
First, we would attempt for a small sample and then increase it to high volume (MP) if the product passes all tests throughout the development phase.
Reference #268308 for specs and pricing.
Silicon Nitride Wet Etching
A materials scientist requested the follwoing quote:
I’m interested in the SiN coated wafer, I have some questions:
- Is it double side SiN coated? Is the bottom side protected by SiN? What’s the roughness (hight) of the backside Si?
- 2. All the Si wafer are single side polished,is any option for double side polished?
- 3. What’s the estimated stress of the SiN layer of Standard LPCVD process? (I expected medium or higher stress).
I need 4” and prime quality, 100nm - 400nm SIN fine for me, 500 microm thickness wafer. Btw, is there intrinsic Silicon wafer?
I was searching on the Nitride silicon page. Ideally yes. That’s what I want.
The problem is I can not decide if I need DSP or SSP, since I don’t know if the silicon nitride can fully cover the backside of the single polished Si wafer.
Si Item #3193
100mm Undoped <100> >10,000 ohm-cm 525um DSP Prime
If the answer is yes, I would like to have the item 3913, since its in stock. I want use the backside SiN as protect layer for backside wet etching.
Reference #253387 for specs and quantity.
Wet Etching Services
A corporate researcher requested a quote for the following:
Can you provide or do you have contacts that can provide wet etching services? We have some specific conditions that we use to wet etch wafers. The process is similar to this
described here. We would want
100mm wafers etched in this manner. We are etching silicon, there is no mask. We use voltage and time to control the etching. Volume is small now but could grow significantly.
UniversityWafer, Inc. Replied:
Do you etch the whole wafer surface or through a mask? Is it MEMS type of controlled depth etching of membranes or similar structures? And of course, what is the volume and future potential?
Reference #121129 for specs and pricing.
Quartz Used For Isotropic Wet Etching
A graduate student requested a quote for the following:
I have on idea which orientation to pick up. I need some thin quartz wafer for the isotropic wet etching. I need your advice.
I need the quartz wafer for the isotropic wet etching. Should I pick up single crystal quartz or fused quartz?
The sharp can be a square , the length is about 10mm to 15mm, the thickness is about 500um. One side polished. I need to know the price and then decide to buy how many.
UniversityWafer, Inc. Quoted:
| Inquiry No | Crystal Material | Diameter | Thickness | Surface Finish |
| 126414 | Fused Silica (JGS2) | 10*10mm | 0.50mm | SSP |
| 126414 | Fused Silica (JGS2) | 15*15mm | 0.50mm | SSP |
Reference #126414 for specs and pricing.
What is Wet Etching?
Wet etching is a process used in semiconductor manufacturing to remove material from a substrate using liquid chemicals. This process involves immersing the substrate in a chemical solution that reacts with and dissolves the material to be removed. Here are the key aspects of wet etching:
Process
- Preparation: The substrate is first coated with a photoresist material, which is then patterned using
 photolithography to expose the areas to be etched.
photolithography to expose the areas to be etched. - Etching: The substrate is immersed in a chemical etchant solution that selectively reacts with the exposed material, dissolving it away. The photoresist protects the areas that are not to be etched.
- Rinse and Dry: After etching, the substrate is rinsed to remove any remaining chemical solution and then dried.
Advantages
- Selectivity: Wet etching can provide high selectivity, meaning it can differentiate well between the material to be etched and the underlying or adjacent materials.
- Cost-Effective: The process is relatively simple and cost-effective compared to other etching methods.
- Smooth Surfaces: It often produces smooth etched surfaces, which can be advantageous for certain applications.
Disadvantages
- Isotropic Etching: Wet etching typically etches isotropically, meaning it etches uniformly in all directions. This can lead to undercutting where the material under the photoresist is also partially etched.
- Limited Precision: The process may not provide the same level of precision and control as dry etching techniques like reactive ion etching (RIE).
Common Etchants
- Hydrofluoric Acid (HF): Used for etching silicon dioxide (SiO2).
- Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4): Used for etching silicon nitride (Si3N4).
- Nitric Acid (HNO2) and Acetic Acid (CH3COOH): Used in combination for etching silicon.
Applications
Wet etching is commonly used in the fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), the removal of oxide layers, and the patterning of thin films in semiconductor devices.
Overall, wet etching is a fundamental process in semiconductor fabrication, valued for its simplicity and effectiveness in various applications.
300 Micron Silicon Wafers for Wet Etching
A PhD candidate requested a quote for the following:
Let me explain you in more detail. I need 6 wafer of 300 um thickness with 4 " in diameter. I would use these wafers for wet etching from back side. so i need to have etch stop layer. either sio2 or SiN. I think 1 um SiO2 could be enough for 300 um. If not I would need higher thickness of SiO2 on wafers. Again I wanted to have the quotation for the silicon wafer with sputtered SiN to compare to price. this means at the end i have to choose one among the three options, i.e.:
- 6 bare 300 um silicon wafer with 4" in diameter
- 6 300 um silicon wafer with 4 " in diameter with 1 um SiO2 on both sides
- 6 300 um silicon wafer with 4 " in diameter with enough thickness of SiN for wet etching of silicon on both sides
Reference #107150 fo specs and pricing.
Wet Etching Jobs
Silicon (senior) Process Engineer:
The position serves as a process engineer to fabricate silicon based optoelectronic devices in Class 100 or similar microfabrication clean room facilities. Candidate must have silicon and related materials (e.g. silicon oxide etc.) processing experience such as PECVD, plasma dry etching, wet etching, metal sputtering and furnace operation. Knowledge of processing equipment maintenance and qualification is a plus. PhD or M.Sc in electrical engineering, material science and engineering, applied physics or related fields is expected.
Anisotropic Wet Etching
A PhD student researchign amorphous materials requested the following quote:
I want to ask that do you have silicon wafer after Anisotropic Wet Etching? I see an orientation of your wafers, but i am not sure what are those? Does is mean all your wafers are anisotropic? Sorry i am not very familliar with this. Maybe you can call me to discuss in detail?
UniversityWafer, Inc. Replied:
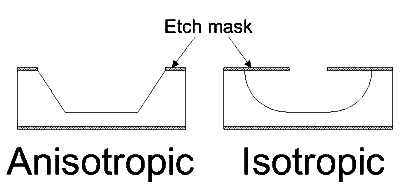
5. Silicon Wet EtchingIn general, there are two classes of etching processes:
Wet etchingWet etching is a blanket name that covers the removal of material by immersing the wafer in a liquid bath of the chemical etchant. Wet etchants fall into two broad categories; isotropic etchants and anisotropic etchants.
Anisotropic and Isotropic Etch Mask Silicon, exhibit anisotropic etching in certain chemicals. Anisotropic etching in contrast to isotropic etching means different etch rates in different directions in the material. The classic example of this is the <111> crystal plane sidewalls that appear when etching a hole in a <100> silicon wafer in a chemical such as potassium hydroxide (KOH). The result is a pyramid shaped hole instead of a hole with rounded sidewalls with a isotropic etchant. Plane hkl etching speed: Vhkl =dhkl / t where: dhkl - etching deep, t - etching time EXAMPLE: Silicon membrane
W = a0 + 21/2 x (d-m) - 2u where: u = (V111 x t)/sinQ, Q = 54.74° The last set of 4 images is what can be etched with Anisotropic (KOH) etch on a (110) wafer. The 4 cases are for different orientations of positioning of a rectangular mask. Reference #264316 for specs and pricing. |