What Bandgap to Generate Underwater Solar Energy?
A PhD candidate researching underwater solar energy requested help with their project.
Hi there. Hope you're doing well. Our group is focusing on the harvesting of solar energy underwater. We are looking for the supply of photovoltaic cells having a bandgap in the range of 1.8eV to 2.3eV in order to optimize solar energy. Preferably looking for Indium Gallium Phosphide, Gallium Arsenide. We would like to know if you have a product which can suffice our need? We would also like if we could get a quotation for same with delivery time. Awaiting your response.
I require a solar panel to power a simple module and function underwater. Size must not exceed 1 sq.m, Output Voltage around 12V, and Bandgap between 1.8eV to 2.3eV, specifically looking for GaInP/GaAs/Ge Triple Junction cells.
UniversityWafer, Inc. Quoted:
We did literature study before preparing the offer. Because the testing and the final product water depth are different, two different kinds of panels, each one designed for a different depth of water, are advised to use. For shallow water the panel with TJ cells are recommended to use and for deeper water, the panel with DJ cells are recommended to use. Our offer is valid for DJ or TJ, price is the same for both.
Please check attached the water absorption spectrums from the different sources in the literature. Each has minor differences but generally limited by the 20m for IR radiation. Besides, the band gap (1.8eV to 2.3eV which is between 540nm to ~690nm) doesn’t match conventional TJ cells. Please also check out the band gap diagram from the attached figures. Germanium junction (band gap 0,7eV) will not produce so much and may cause more losses than what it brings. So, we recommend Dual junction made of GaAs/ (Al)GaInP which is best fitting to your requirements.
Additional notes: Usually sea water absorption spectrum may not allow Germanium junction to produce enough efficiency (<1%) due to IR absorption of the water surface (only Works in the dept less than a few meters). Therefore our offer also includes DJ which can also work almost without a significant change in the efficiency similarly to TJ. Since we don't know the power consumption and current requirements or AC/DC operation etc. of the customer module to be powered by the panels we prepared a standard generic solution. Please let us know if the customer has additional requirements like inverter etc. They can be subject to separate quotes from us.
We quote:
Item Qty. Description
HF91. 1 Triple junction or Dual Junction SC
for 1.8eV to 2.3 eV.
Min 10 cells, 12V output, panel size< 1sqm
Optional:
Item Qty. Description
HF91b. 1 Special Encapsulation for
underwater use. Water resistant,
Anti-Algae coating, waterproof
Electrical sockets
Item Qty. Description
HF91c. 1 Fresnel Lens Concentrator Module
mounted on panel.
Reference # 257878 for specs and pricing.
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
What substrates are used to Fabricate Semiconductor Electronics?
Semiconductor electronics are fabricated on a variety of substrates, depending on the specific application and requirements of the device. The most commonly used substrate for semiconductor electronics is silicon, due to its abundance, low cost, and well-developed fabrication processes. Other commonly used substrates include germanium, gallium arsenide, and indium phosphide.
Silicon is the most widely used substrate for semiconductor electronics due to its excellent electrical properties, as well as its availability and low cost. Silicon wafers are typically used as the substrate for the fabrication of integrated circuits and other semiconductor devices.
Germanium is another common substrate material, particularly for high-frequency applications. It has a higher electron mobility than silicon, which makes it suitable for use in transistors and other high-speed devices.
Gallium arsenide is a popular substrate material for high-power and high-frequency applications, as well as for optoelectronics and infrared devices. It has a higher electron mobility than both silicon and germanium, which makes it suitable for use in high-performance devices.
Indium phosphide is another substrate material used in semiconductor electronics, particularly for high-speed and high-frequency applications. It has a higher electron mobility than both silicon and germanium, which makes it suitable for use in high-performance devices.
In addition to these materials, other substrate materials are also used in semiconductor electronics, such as silicon carbide, diamond, and various compound semiconductors. The choice of substrate material depends on the specific requirements of the device and the application, as well as the availability and cost of the substrate material.
Semiconductor Devices
Here are the Top Ten Semiconductor Devices ranked by widespread application and commercial significance, along with their typical use cases:
Top 10 Semiconductor Devices by Application
| Rank |
Semiconductor Device |
Primary Applications |
| 1 |
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) |
Used in CPUs, GPUs, power supplies, digital logic, and automotive systems. |
| 2 |
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) |
Common in analog circuits, audio amplifiers, and switching circuits. |
| 3 |
PN Junction Diode |
AC to DC conversion, voltage regulation, and signal demodulation. |
| 4 |
Light Emitting Diode (LED) |
Lighting, display technology, indicators, and photonic communication. |
| 5 |
Photodiode |
Used in solar cells, light sensors, and fiber-optic data transmission. |
| 6 |
Thyristor (Silicon Controlled Rectifier - SCR) |
Industrial motor control, HVDC systems, and power grid switching. |
| 7 |
Zener Diode |
Voltage reference, surge suppression, and circuit protection. |
| 8 |
Tunnel Diode |
Microwave oscillators and ultra-fast switching applications. |
| 9 |
Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) |
Electric vehicles, motor drives, and solar inverters. |
| 10 |
CMOS Logic Gates (AND, OR, NOT, etc.) |
Fundamental building blocks of digital circuits, used in all ICs. |
Video: Learn About Band Gap and Semiconducotr Current Carriers
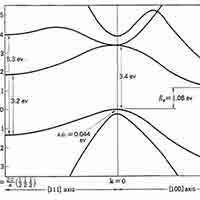
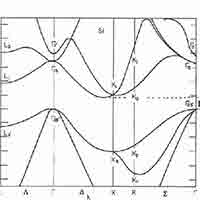
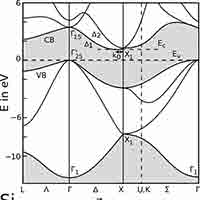
What is a Silicon Band Structure?
The silicon band structure is a graphical representation of the energy levels (or "bands") that electrons can occupy in a silicon crystal, as a function of their momentum. It is a fundamental concept in solid-state physics and semiconductor engineering because it determines how silicon conducts electricity and how it interacts with light.
Key Elements of Silicon’s Band Structure:
-
Valence Band:
-
Conduction Band:
-
Band Gap (Eg):
-
The energy difference between the conduction band minimum and valence band maximum.
-
For silicon, the band gap is about 1.1 eV at room temperature.
-
This is a "forbidden" energy range where no electron states exist.
-
Indirect Band Gap:
-
Silicon has an indirect band gap, meaning the lowest point in the conduction band and the highest point in the valence band occur at different momentum values (k-values).
-
This makes optical transitions (like light emission) less efficient in silicon, which is why it’s not used in LEDs.
-
Brillouin Zone:
-
The band structure is plotted within the first Brillouin zone, which is the fundamental region of wave vectors in a crystal lattice.
-
Common paths in the silicon band structure include points labeled Γ, X, and L.
Visualization:
A typical silicon band structure diagram will show:
-
Energy on the vertical axis (in electron volts, eV)
-
Crystal momentum (k-vector) on the horizontal axis
-
Curves representing the allowed energy levels for electrons
Key Features Explained
- Valence Band Maximum (VBM): Located at the Γ point (center of the Brillouin zone), representing the highest energy level of the valence band.
- Conduction Band Minimum (CBM): Occurs near the X point, not at the Γ point, indicating that silicon has an indirect band gap.
- Band Gap (Eg): Approximately 1.1 eV at room temperature, representing the energy difference between the VBM and CBM.
- Indirect Band Gap: The mismatch in momentum between the VBM and CBM means that electron transitions between these bands require a change in momentum, typically facilitated by phonons. This property makes silicon less efficient for light emission applications like LEDs.
What is the Band Gap of Silicon Substrates
The band gap of Silicon (Si) is approximately 1.12 eV 1.12 eV (electron volts) at room temperature. It's important to note that silicon has an indirect band gap, which has implications for its optical properties, particularly its relatively poor efficiency as a light emitter.
Various methods, including electrical conductivity, Hall effect, photoconductivity, and optical absorption, can 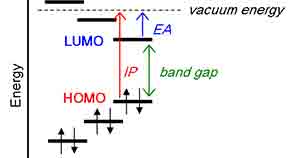 determine the bandgap of a semiconductor. These methods vary in their ability to provide accurate data and are influenced by the material's temperature, surface, and structural properties. However, the optical absorption method provides results that are less affected by these factors and is, therefore a preferred technique.
determine the bandgap of a semiconductor. These methods vary in their ability to provide accurate data and are influenced by the material's temperature, surface, and structural properties. However, the optical absorption method provides results that are less affected by these factors and is, therefore a preferred technique.
This method can be used to determine the direct and indirect band gaps of crystalline semiconductors such as GaAs, Si, and Ge. It is particularly useful for amorphous and powder-like samples because it can be performed at much lower energies than traditional measurement-analysis methods. In addition, the method is immune to the effects of experimental details such as accidental optical misalignment and improper spectra correction.
Wide bandgap materials like gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) have significantly higher breakdown fields than standard silicon, enabling power components to operate at higher voltages, faster speeds, and greater efficiencies.
What Is the Band Gap in Semiconductors?
In semiconductors, the band gap is the energy needed to excitably bind an electron from the 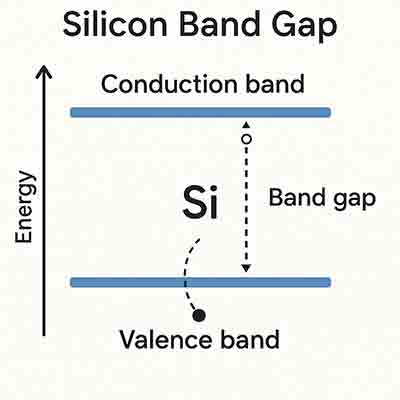 valence to the conduction band. When photons with sufficient energy pass through, an electron is freed and participates in conduction. A hole is created where the formerly bound electron was.
The band gaps are fairly well defined for intrinsic materials, such as crystalline silicon wafers. However, for amorphous materials, the band gap is more complex.
valence to the conduction band. When photons with sufficient energy pass through, an electron is freed and participates in conduction. A hole is created where the formerly bound electron was.
The band gaps are fairly well defined for intrinsic materials, such as crystalline silicon wafers. However, for amorphous materials, the band gap is more complex.
What is the Band Gap of Silicon Wafers?
The band gap of a semiconductor is the difference between the energy required for electrons to jump from the valence to the conduction bands. This energy is measured in electron Volts (eV). The larger the band gap, the more the material can conduct electricity. Similarly, the smaller the band gap, the more the material can insulate.
Why is it important?
The band gap is important because it allows electrons to flow across the material. If the valence and conduction bands were entirely separated by energy, it would be impossible for electrons to pass from one band to another. However, suppose there is sufficient energy available in the valence band. In that case, it can be used to promote the transfer of an electron from an unoccupied state (known as an atomic orbital) to the conduction band, and is known as excitation. When this occurs, it creates an electron hole. Electrons in the conduction band can then move freely within the crystal lattice and conduct current.
In contrast, insulators have significant forbidden gaps in energies that prevent electrons from the valence band from jumping up into the conduction band and participating in conduction, and this is why insulators are so bad at conducting electricity. In contrast, semiconductors have smaller band gaps and can efficiently work electricity.
To produce a semiconductor with a desired band gap, engineers use a process called bandgap engineering. This involves altering the chemical composition of a semiconductor alloy to achieve the appropriate energy transition of atoms in the crystal lattice. It is essential to develop optoelectronic devices such as photodiodes and solar cells. In the case of silicon, it is possible to engineer a wide range of band gaps by increasing or decreasing the concentration of certain elements in the crystalline structure.
What Applications are Silicon Band Gap Essential?
A semiconductor is an electronic material with closely spaced energy levels, allowing electrons to jump between them with relatively little energy, and makes it a good conductor at normal temperatures. A gap between the top of this valence band and the bottom of the conduction band provides the necessary energy for the electrons to make this interband transition.
The width of this gap determines a material's color, with light-absorbing materials appearing black and emitting ones appearing white. This is because the energy of the absorbed photon is much less than the difference between the bands. Moreover, the position of the bands determines whether they are direct or indirect. Direct bandgap materials absorb light strongly, while indirect ones emit light weakly unless doped with suitable atomic ions.
Wide-band gap (WBG) semiconductors have a larger E g than conventional semiconductors, such as silicon and germanium, and means that they can be used for more efficient light-emitting diodes and lasers, as their higher transition energies allow them to operate at higher temperatures, where the electrons need more power to generate carriers through impact.
WBGs can also be used to reduce transistors' size and power consumption, as they require less voltage to operate at their optimum switching speeds, and is especially important for radio applications, where a single device can be used to carry both the signal and the radio-frequency components of a system, eliminating the need for separate transmitters and receivers.
What is the Silicon Band Gap Energy?
In physics, the term band gap refers to the energy difference between the upper layer of a semiconductor’s valence band and the lower layer of its conduction band. This energy difference is measured in electron volts (eV), representing the range of energies that cannot be transferred between these two layers.
Silicon has a band gap energy of 1.1 eV, meaning it can absorb photons with an energy of up to 1100 nm. This energy can cause an electron to jump from its valence band into the conduction band, creating electricity. This energy can also be used to make photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity.
Physicists have discovered some materials with narrower gaps between valence and conduction bands. These are called semiconductors and can behave like metals or insulators, depending on how excited they are.
One of the best-known examples of a semiconductor with a narrow band gap is silicon. However, many researchers have been experimenting with new materials with even smaller gaps. These new materials could be used to create novel optical fibers that can be filled with gasses or liquids for nonlinear processes.
Related Pages