Fabricate Low Temperature BEOL Schottky Contact Diodes
A PhD student a PhD student requested the following quote:
We need Si wafers with a layer of n type doped amorphous Silicon on top (1e18- 1e19). Do you have or do you offer any wafers matching this description?
We are planning to make low temperature BEOL compatible schottky contact diodes out of the low temperature Si (a-Si) doped Si. Our previous work demonstrated this with phosphorous doped c-Si and poly-Si (600 C deposited Si). We now plan to see if it works for low temperature (below 400 C) a-Si for BEOL compatibility.
The ideal stacks of films (from bottom to top) we are looking for are as follows:
- 4" Si wafer; P type; 100 crystal orientation; 1-20 ohm-cm resistivity; SSP; Test grade
- Thermal Oxide of 1000 A on both sides of the wafer
- Low temperature Si (Amorphous Si) of thickness in between 1000-2000 A and with n-type doping of different doping concentration of around 1e+18 and 1e+19 /cm3 on the top of the wafer.
Reference #273070 for specs and pricing.
Silicon (c-Si) Wafers
The advantages of using Crystalline silicon (c-Si) substrates includes having lower absorption in the visible range .
The metasurface is fabricated on a commercially available 230 nm thick c-Si (100) epitaxially grown on a sapphire substrate (from UniversityWafer, Inc.)
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
Sapphire + Crystallane Silicon (c-Si)
Researchers have used the following wafer for their hologram research.
Sapphire + crystallane silicon (c-si):
Silicon on Sapphire (SOS) wafer
SOS (thickness: 230nm) Ø4'' R+/-0.5deg DSP Sapphire Sub 460+/-20um with <100> orient. Si epi film
230nm+/-10%,the Resis. >100 Ohmcm
$/ea Please contact us for pricing.
P.s also 100nm ~ 3000nm SOS wafer available to supply
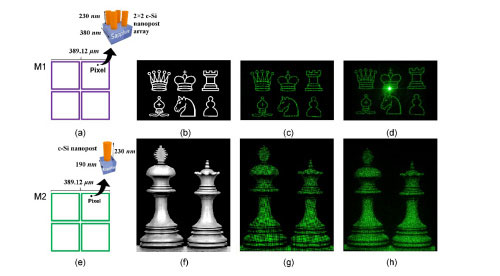
Fabricated Metasurface Holograms
C-Si for High Efficiency Solar Panels
A PhD candidate working on Silicon solar cell preparation requested a quote for subtrates for his research.
We need 6 inch Amorphous Silicon wafer cell with ITO on top and bottom. We require a-Si:H/c-Si HJ 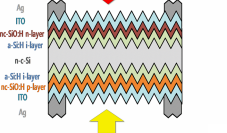 solar cell fabricated. The pictures given below are a reference. A 6-inch wafer is preferable. We need 100 wafers but initially, we want to begin with 10 wafers. I have also attached the paper that has the method section with this structure fabrication for reference.
solar cell fabricated. The pictures given below are a reference. A 6-inch wafer is preferable. We need 100 wafers but initially, we want to begin with 10 wafers. I have also attached the paper that has the method section with this structure fabrication for reference.
Over 30% efficiency bifacial 4-terminal perovskite-heterojunction silicon tandem solar cells with spectral albedo.
Reference #267123 for specs and pricing.
What is Crystalline Silicon (C-Si)?
C-Si is a silicon cell. It is an excellent alternative to conventional solar cells. It is also highly efficient, but costs a little more. In order to make a good solar panel, it should be sized properly and should be efficient. Several factors affect the efficiency of a solar cell. The first factor is the size of the panel. The larger the panel, the more energy it can produce. A smaller panel can be more expensive than a larger one, but can be more efficient.
Monocrystalline silicon is the most common form of PV materials, and it has many advantages over its 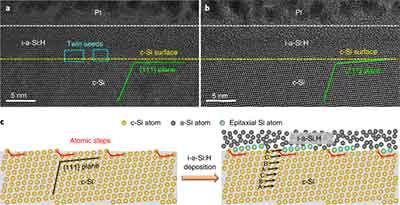 amorphous counterpart. Its light weight and easy fabrication make it a very useful material for solar panels. In addition, it is amenable to improvements in capex processes. As a result, its efficiency is increasing all the time. This makes it an excellent material for rooftop solar panels, and it is also the most expensive.
amorphous counterpart. Its light weight and easy fabrication make it a very useful material for solar panels. In addition, it is amenable to improvements in capex processes. As a result, its efficiency is increasing all the time. This makes it an excellent material for rooftop solar panels, and it is also the most expensive.
There are two types of silicon: a-Si and c-Si. While monocrystalline silicon has more efficiency than a-Si, both are used in photovoltaic technology. In photovoltaic systems, crystalline silicon is used to create solar cells. Solar panels are assembled into solar panels. There are several advantages of both types of materials. If you are wondering which one is right for your project, keep reading! You'll soon find out!
Despite the similarities in structure, both crystalline and allotropic silicon have their own distinct benefits. They are both light weight, easy to fabricate, and amenable to capex processes. They also both have high efficiencies that make them reliable and cost-effective. The applications for both materials continue to grow. If you are wondering, "What is c-Si? ", you've come to the right place.
A-Si is the oldest thin-film technology. This technology involves chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to place a thin layer of silicon on a substrate. This type of silicon absorbs a wide range of light and performs well even in low light, but a-Si is not as efficient as c-Si, and it isn't recommended for portable solar applications.
Another type of c-Si is microcrystalline silicon, or nanocrystalline silicon. Both are types of amorphous silicon, with small crystalline-silicon grains separated by grain boundaries. Although c-Si is the most common type of semiconductor, nano-Si is the more common type. Its name comes from the fact that it is a fine-grained form of polysilicon.
Nanocrystalline silicon is a form of silicon. It is allotropic, and it is the most common type of amorphous silicon. In contrast, polycrystalline silicon contains tiny crystalline-silicon grains that are separated by grain boundaries. It is best used for applications that require fine-grained components. However, this type of silicon is a good choice for applications that require a narrow grain-size.
Another type of silicon is called nanocrystalline. This type is amorphous and is not crystalline. It is amorphous, but is also the most popular type of silicon. It is amorphous, and is formed in the same way as amorphous silicon. It is amorphous, which means that it is an amorphous form of silicon. While it is not a crystalline material, it is amorphous.
The amorphous phase of silicon is amorphous. The amorphous phase is the most common type. It has no grain boundaries, but contains many crystalline-silicate particles. Amorphous silicon is amorphous, and its grains are separated by grain boundaries. This is why it is often used in electronics. Its properties are similar to crystalline silicon, but can be made up of nanocrystalline layers.
CIS solar cells can be combined in tandem solar cells. The difference between them is that the former has better stability and resistance to shading. The latter is more efficient than amorphous silicon, and is therefore a good alternative for residential and commercial solar applications. The amorphous and protocrystalline silicon solar cell are best for short-wavelength light. Long-wavelength light is absorbed by the amorphous silicon substrate.
Amorphous silicon is made of amorphous silicon and contains large, irregular silicon grains. Amorphous silicon is the most common type of crystalline-si solar cells, but there are other types of the material as well. It is also used in thin-film solar cells. As a result, these solar cells are less efficient than their amorphous counterparts. It is difficult to control the amorphous form, and thin-film modules require more surface area.
Silicon C-Si Wafers
South Korean scientists have developed a sustainable process to recover silicon wafers from old solar cells and build new solar cells from the recovered silicon. Traditionally, multicrystalline silicon solar cells are made from square silicon substrates, which are cut from ingots cast in quartz crucibles. [Sources: 3, 6]
The use of Si-110 wafers would allow surface splitting and the production of high-efficiency solar cells. The advantage of this preferred embodiment is that the wafer itself can be used as an alternative to existing silicon wafer manufacturing plants built to process large silicon wafers. PhotonExport supplies small quantities of silicon crystals and waves, as described below, as well as for the production of photovoltaic cells. [Sources: 0, 1]
Si-110 wafers and is available directly from our inventory and for the production of photovoltaic cells and other applications. Si - 110 wafers, but it is also available from inventory through a variety of other sources, such as the U.S. Department of Energy. [Sources: 5]
We select high quality and inexpensive items from the above listed sources, as well as from other sources, such as the U.S. Department of Energy and other manufacturers. Si - 110 wafers from our inventory or from one of the high quality, cheaper items we select from the above. SI-110 wafers from a variety of sources and manufacturers, rather than from the inside out, choosing quality or cheaper products. [Sources: 4]
Chinese Mono Silicon Wafer Manufacturer, Certified Chinese Silicon Manufacturer and Made in China. Chinese mono-silicon wafers from a certified China - made, China made and Chinamade, certified by the U.S. Department of Energy (USDOE), Chinese Silicon manufacturer. [Sources: 4, 5]
The company has a long and well-established history of manufacturing high-quality silicon wafers for use in solar cells and has long-term, reliable and reliable manufacturing facilities. The production of silicon wafers is a complex process and the specialty of UniversityWafer, Inc. is to ensure that the highest quality product is delivered to the customer. The film, hereinafter referred to as SiO2, is grown from evaporated silicon and the impurities that diffuse from silicon to the wafers during evaporation and electrodeposition are monitored during the chipping of the wafer, especially in the case of silicon-based solar cell production, as they can affect the mechanical and optical properties
UniversityWafer, Inc. is a leading supplier of high-quality silicon wafers for the solar cell industry and Tier 1 silicon dedicated to supporting large and small users of silicon products. [Sources: 5]
P-type silicon wafers, which are doped with boron, are suitable for use in solar cells and other high-performance solar cell applications. Silicon wafer suppliers are iso-silicon, silicon c-Si and silicon b-Si, and you can also choose from laser scribing. They have a variety of different standards, including high performance, low cost, high quality and high efficiency, but they all offer the same quality of silicon and high performance for the solar industry. [Sources: 5]
The silicon carbide wafer market is manufactured in Japan and we offer the best deals on silicon wafers at nearby locations. The silicon wafer directory includes Japanese silicon and silicon wafers from Japan and silicon carbide and silicon b-Si from the United States. [Sources: 5]
We understand the silicon wafer market by identifying the different sub-segments and different types of silicon b-Si wafers that are offered for sale. [Sources: 4]
Sources:
[0]: https://www.google.com/patents/US5349207
[1]: https://patguadagno.com/dementia-desiccant-currency/silicon-wafer-100-111.html
[2]: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/426379
[3]: https://www.chemistryworld.com/news/a-bright-future-for-silicon-solar-cell-recycling/9160.article


 amorphous counterpart. Its light weight and easy fabrication make it a very useful material for solar panels. In addition, it is amenable to improvements in capex processes. As a result, its efficiency is increasing all the time. This makes it an excellent material for rooftop solar panels, and it is also the most expensive.
amorphous counterpart. Its light weight and easy fabrication make it a very useful material for solar panels. In addition, it is amenable to improvements in capex processes. As a result, its efficiency is increasing all the time. This makes it an excellent material for rooftop solar panels, and it is also the most expensive.